Health insurance premiums in the U.S. significantly increased between 1999 and 2024, outpacing the rate of worker earnings by three times, according to our newly published research in the journal JAMA Network Open.
Premiums can rise if the…

Health insurance premiums in the U.S. significantly increased between 1999 and 2024, outpacing the rate of worker earnings by three times, according to our newly published research in the journal JAMA Network Open.
Premiums can rise if the…
An international group of scientists led by Professor Marc-Emmanuel Dumas at Imperial College London & CNRS, along with Prof. Patrice Cani (Imperial & University of Louvain, UCLouvain), Dr. Dominique Gauguier (Imperial & INSERM, Paris) and Prof….
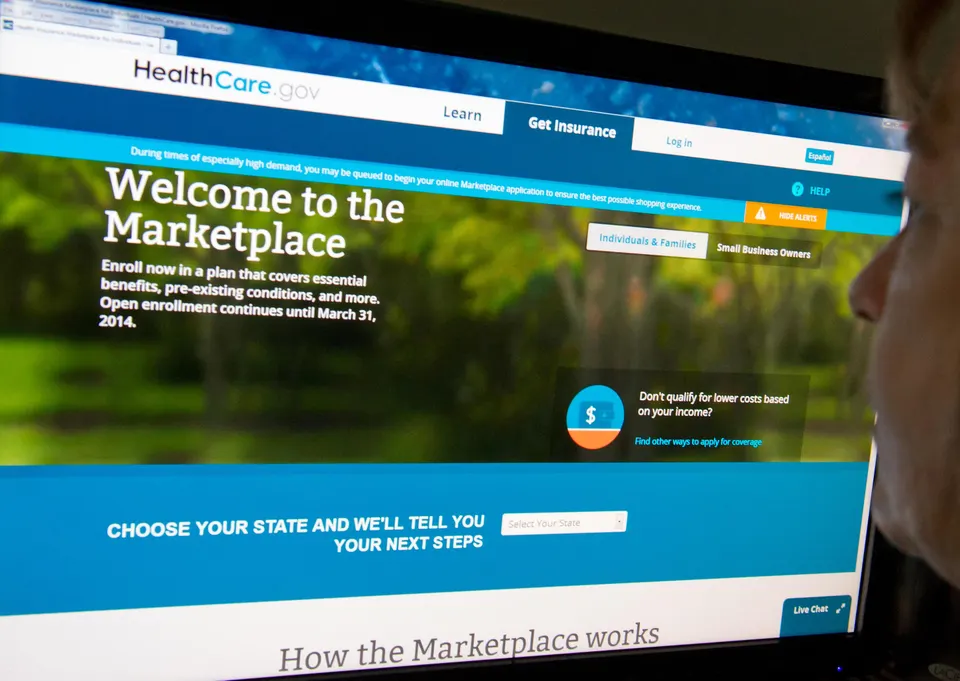
Enrollment in individual coverage under the Affordable Care Act, also known as Obamacare, lags last year’s record pace in new sign-ups, according to figures released by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services on December 5, 2025 for the…

Dr. Retsef Levi speaks during a meeting of the Advisory Committee in Immunization Practices. ACIP is changing its recommendation regarding timing of administration of the hepatitis B vaccine (AP Photo/Mike Stewart)
Copyright 2025 The Associated…
Tantalizing results from small trials and anecdotes raised hopes that drugs like Ozempic could help. Despite setbacks, researchers aren’t giving up yet.
A Mayo Clinic study reports that current genetic screening guidelines fall short in identifying the majority of individuals with familial hypercholesterolemia, an inherited condition that can lead to extremely high cholesterol and early heart…

The National Institutes of Health awarded 22% fewer grants this year under the Trump administration than it has in typical previous year. Yep, only 12,588 NIH grants versus the average of 16,099 per year from 2015 through 2024, according to an…

Many people assume a bowl of kale automatically counts as a nutritional powerhouse. However, without the right companion ingredient, that leafy salad may not deliver the benefits you expect.
Fortunately, there is an easy fix.
Researchers at the…
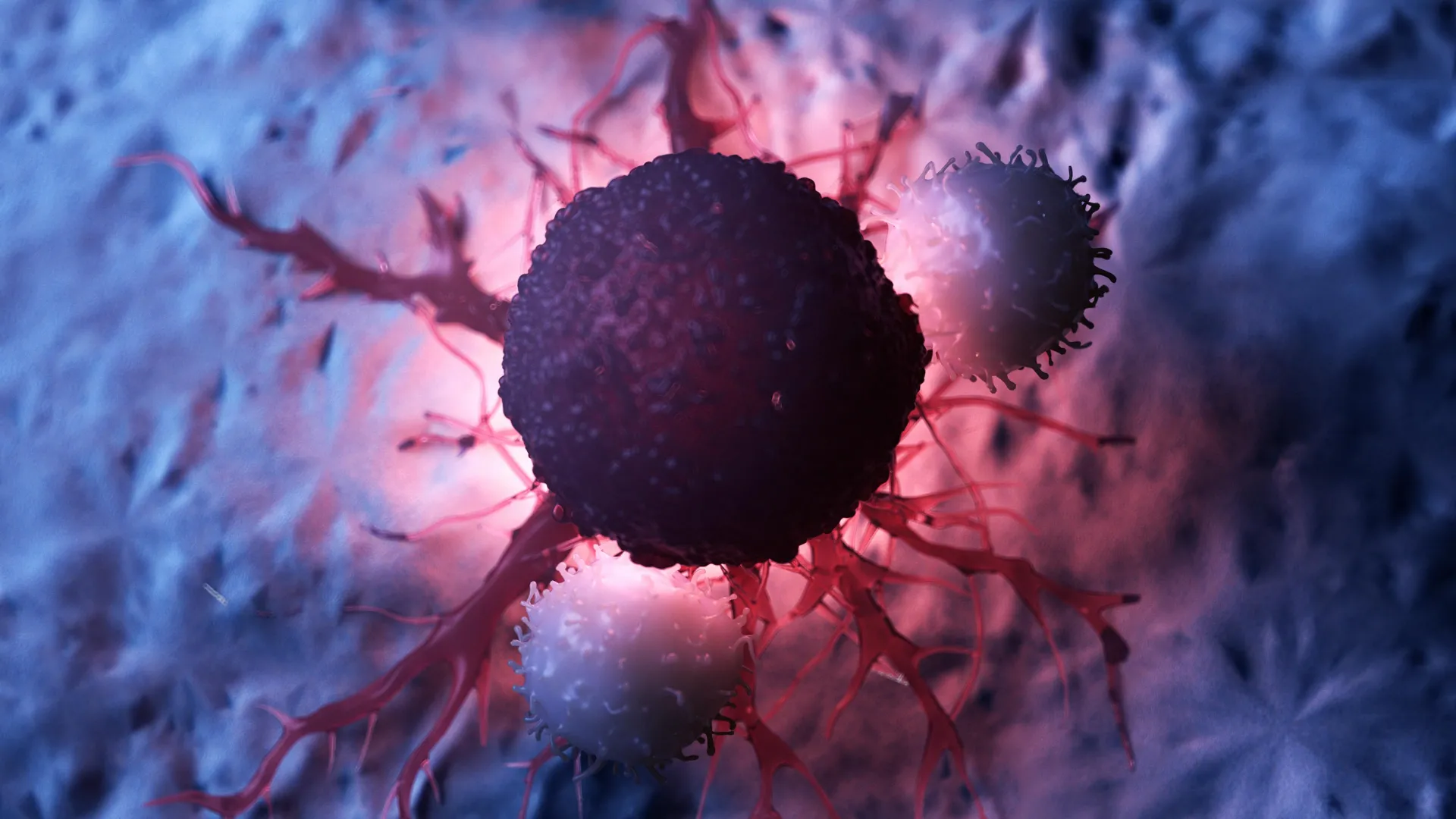
A recent study reports that using reduced amounts of approved immunotherapy for malignant melanoma may lead to better control of tumors while also limiting side effects. The findings come from researchers at Karolinska Institutet and were…

A study published in the scientific journal Communications Earth & Environment proposes that volcanic activity may have contributed to the rapid movement of the Black Death across medieval Europe. According to the researchers, cooling associated…